Skip to main content Preporcessing
Import all needable libraries: torch, matplotlib, pandas and etc.
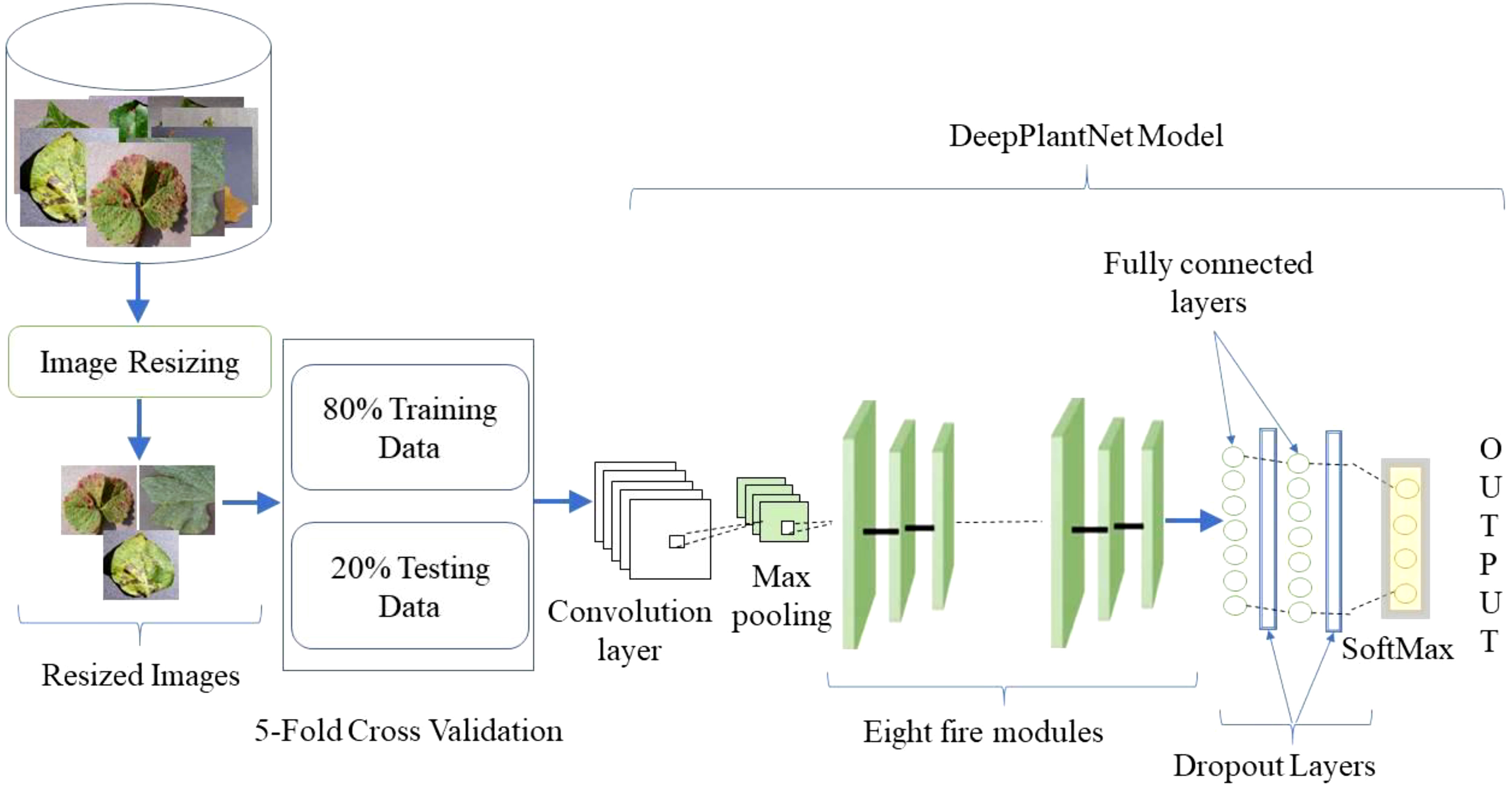
The dataset is split into training (80%), validation (10%), and test sets (10%) using random_split.
Data loaders are then created for each subset, with a batch size of 14 for training and validation, and 1 for testing. Model Selection
The ResNet18 model is loaded using timm, with timm.create_model(). The model is initialized with pretrained weights, and the number of output classes is set to 8 (indicating there are 8 types of leaf conditions). Loss Function and Optimizer
The loss function used is CrossEntropyLoss, appropriate for multi-class classification. The optimizer is Adam, with a learning rate of 3e-4. Training Loop
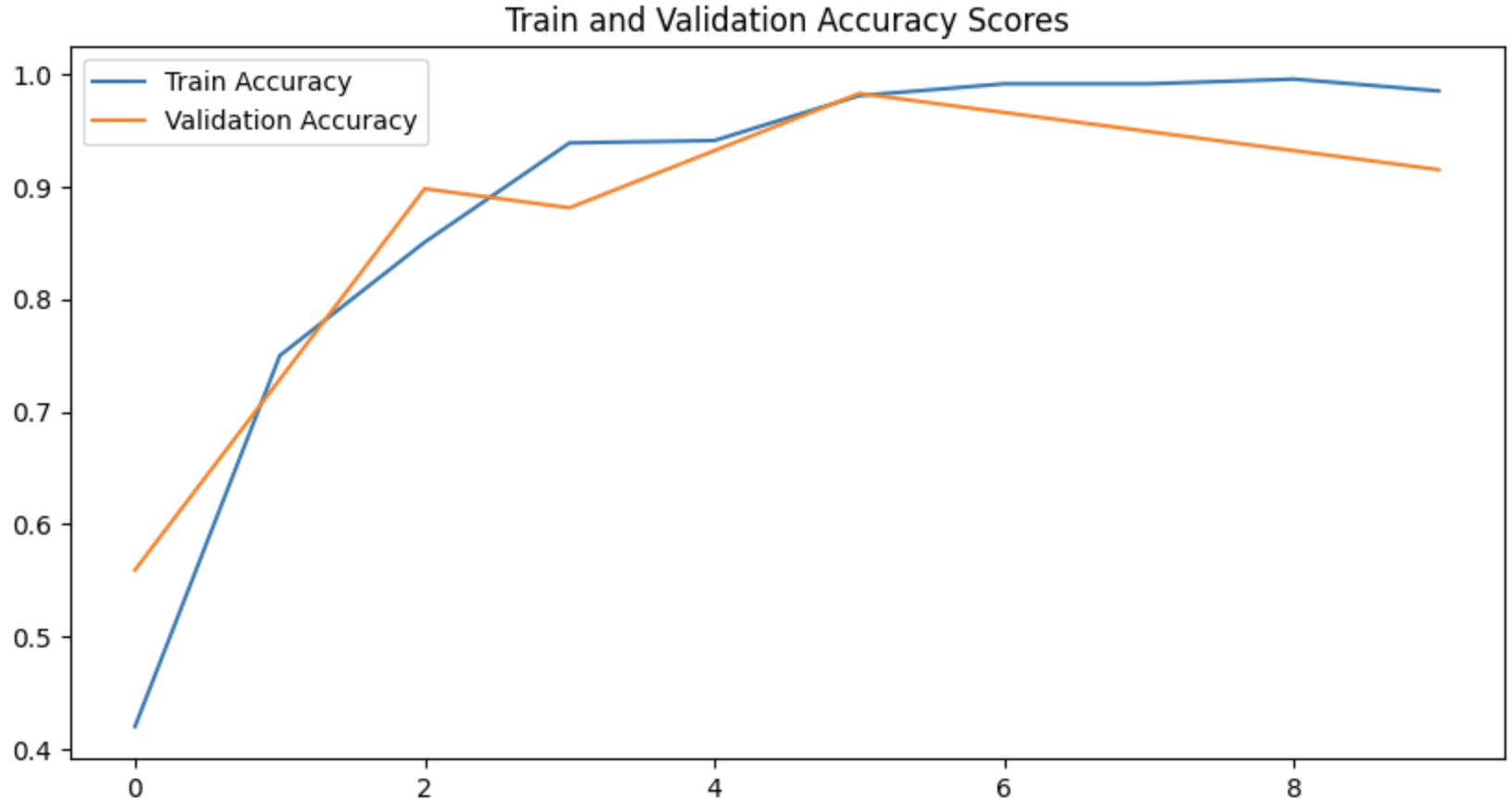
The training loop runs for 10 epochs. Each epoch involves both training and validation phases. The model parameters are updated using backpropagation during training. Validation is performed without gradient tracking, and the validation loss and accuracy are recorded. Prediction and Visualization
The code iterates through a batch of images and predicts their classes. Predictions are compared to actual labels. The result and prediction for random samples are visualized using matplotlib. Training and validation accuracy scores are plotted.